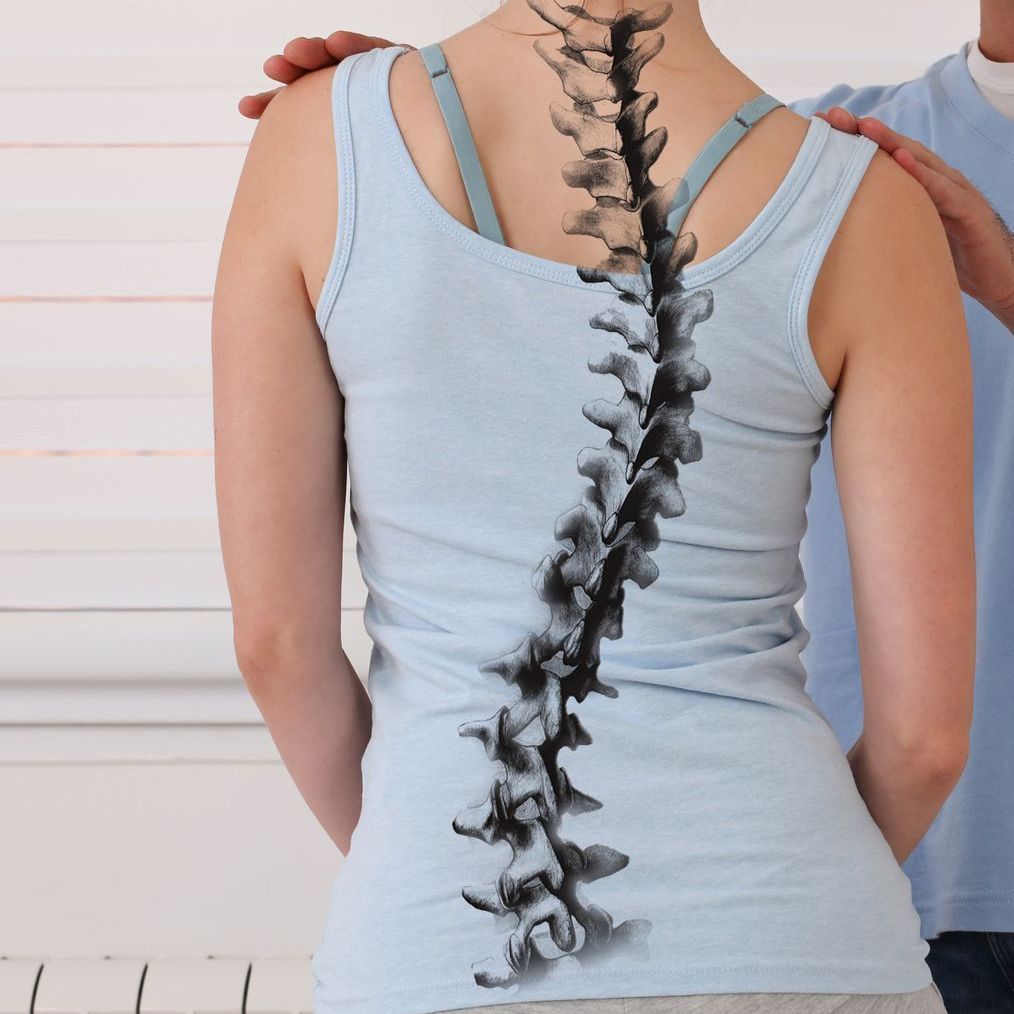
Holistic spine, disc and joint therapies for your long-term back health
Scoliosis therapy for children, adolescents and adults
Targeted side-effect-free regeneration for spinal and joint conditions
Specialized therapies for sports and dance-related injuries and overuse
Prevent illnesses & accelerate healing with vitamin infusions
Stay balanced with Tradtional Chinese Medicine & spinal acupuncture
Spinal, disc, joint and scoliosis surgeries - OA Dr. Jiresch - 1010 Vienna